Dec 03, 2024 | 549 words | 5 min read
13.3.1. Task 1#
Introduction#
Cylindrical steel tanks have many outdoor uses. They are used in oil and gas refining, food production, farming, liquified gas storage, and more! On top of that, these tanks can have various shaped end caps such as flat, elliptical, or spherical.
Your company uses cylindrical tanks with flat end caps (see Fig. 13.1). The tank is an outdoor storage container and will be used to store water. Not only that, the tank has liquid measuring sensors along its height, which alert an operator once the liquid has reached the height of a particular sensor. From these height measurements, the volume of the tank can be calculated. As the sensors are inside the tank, all measurements are internal measurements, so the tank wall thickness is not relevant nor required for this application. When a cylindrical tank with flat ends is installed horizontally, the fluid volume at any fluid height within the tank can be calculated using the function:
Where
\(V_f\) is the fluid volume
\(h\)is the fluid height measured from the tank bottom
\(r\) is the tank radius
\(L\) is the length of cylindrical section of the tank
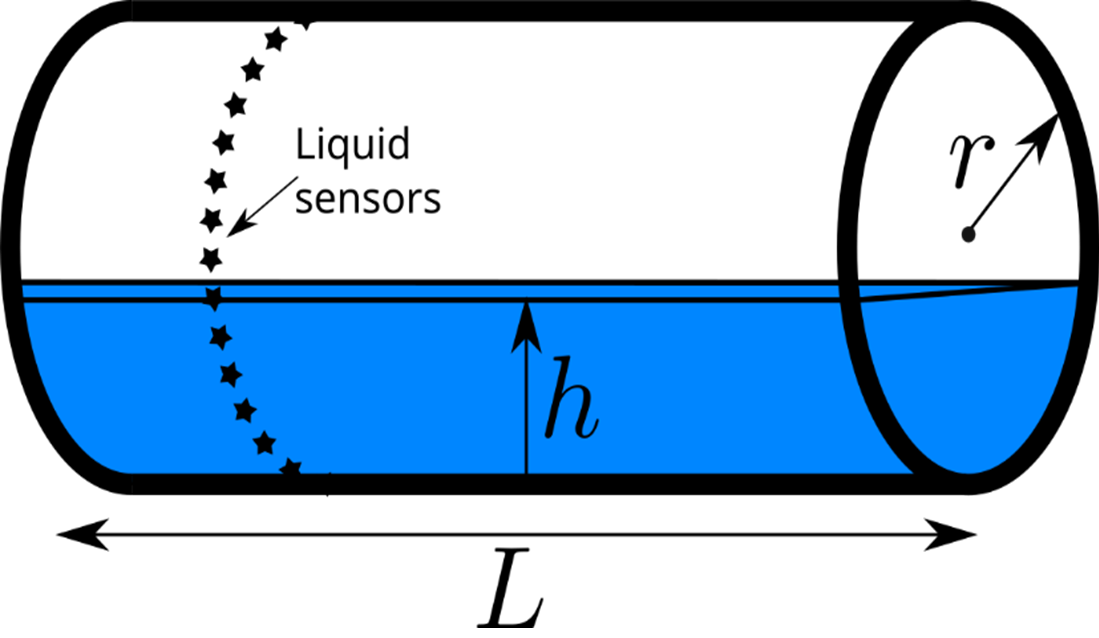
Fig. 13.1 A model of a horizontal cylindrical tank#
Now, you are given a task to design a tank fill measurement system for a tank that is installed horizontally. To be specific, the client wants to be alerted when the volume in the tank is less than 20% of the maximum volume. The fluid height is not measured instantaneously in this system. As the tank is progressively emptied, sensors are tripped, indicating that the fluid has reached the height of a particular sensor.
Task Instructions#
Open up MATLAB and type
editin the Command Window. Then save your file as ma2_ind_1_username.m. Make sure to use the MATLAB Template (ENGR133_MATLAB_Template.m).Write a script that follows the flowchart below to simulate the tank emptying process and meet the safety needs of the system. The script will need a fluid height vector with decreasing increments of \(0.1m\). Then, the script will need to step through the vector while calculating the volume at every height, triggering an alert just after the fluid has fallen below \(20\%\) of the maximum volume.
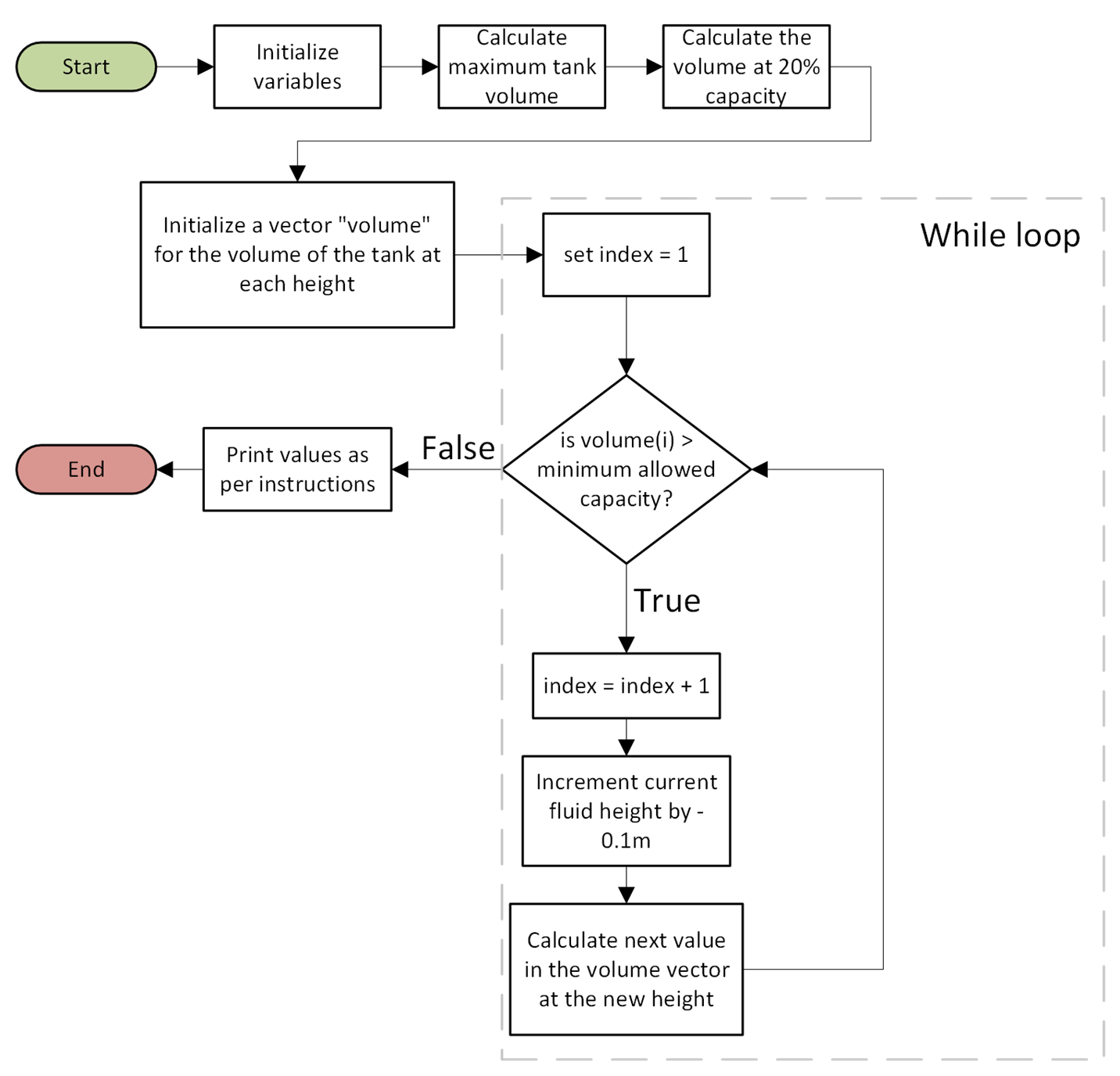
Fig. 13.2 Flowchart for MA2 Individual Task 1#
In the
%% INITIALIZATIONsection, define the testing values as variables:The tank has an inner radius of \(1.25m\), an inner length of \(5.5m\).
Assume the tank starts off completely full when the emptying begins.
The tank has sensors placed every \(0.1m\) in height along the tank.
The client wants to know when the volume of the tank falls below \(20\%\) capacity.
In the
%% CALCULATIONSsection:Calculate the maximum tank volume.
Calculate the tank fill capacity that will trigger an alert.
Create a vector of fluid height values and a vector of corresponding volumes using a while loop.
Hint
In MATLAB, you can gradually increase the size of a scalar variable
xby using a loop. Also, you can initialize the maximum amount of space for an array.Wait, What’s the difference? Where can I see an example? Good question!
Check out https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/matlab_prog/preallocating-arrays.html
Avoid adding elements to the vector when it’s near its capacity; instead, stop just below the limit.
In the
%% OUTPUTSsection, display the number of iterations to fall below \(20\%\) capacity, final fluid height, final fluid volume, and a warning that the volume is too low in a well-formatted print statements.
Publish your script as ma2_ind_1_username.pdf and submit your deliverables to Gradescope.
Sample Output#
Sample Output
>> ma2_ind_1_username Number of iterations = 19 Remaining volume = 4.98 m^3 Fluid height= 0.60 m WARNING: The tank is now below 20% capacity. Please refill.
